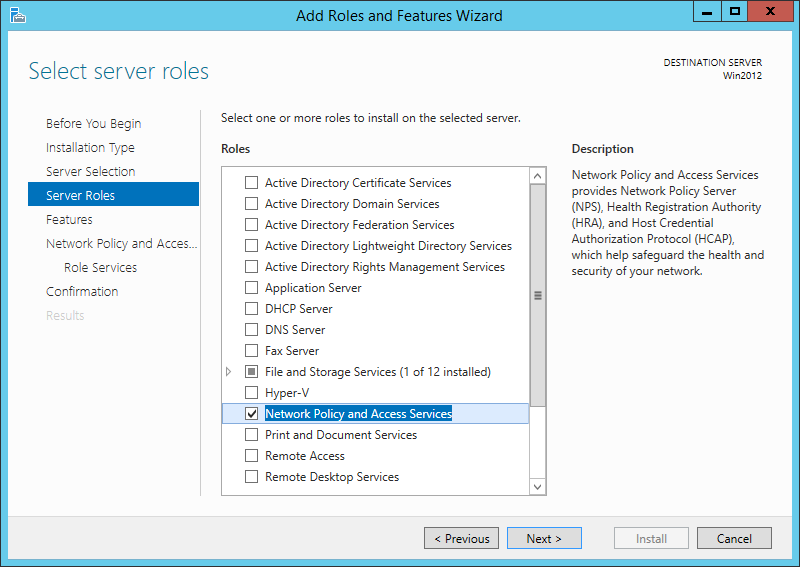
- Microsoft Nps Radius
- Dynamic Vlan Assignment Microsoft Nps Radius Server Login
- Microsoft Radius Server
- Windows Server 2016 Nps Radius
I need to provide remote network access that is restricted depending on the user that dials in (i.e. different users are placed on different VLANs).
I will then implement firewall security (on a separate hardware firewall) between VLANs to restrict what users can access.
Is there any way to assign different users to different VLANs based on their user credentials used during VPN initiation?
NPS 802.1X VLAN Assigment configuration I have been tasked to configure an NPS server to do VLAN assignment based on user authentication credentials. We want for wireless and wired connections to get a VLAN assigned based on the computer account or user authentication. I know 802.1x enough, but not enough to tell you all options. One thing to keep in mind is this. Not all switches support the dynamic VLAN assignment. For example; I now have a Cisco Small Business Wireless Access Point that allows 802.1x authentication, but apparently does not support dynamic VLAN assignment on it.
g18cg18c1 Answer
I think NPS (Network Policy Server / RADIUS) is capable of doing this, however, I'm not sure if it is possible trough VPN:
VLAN Attributes Used in Network Policy
VLAN attributes used in network policy
When you use network hardware, such as routers, switches, and access controllers that support virtual local area networks (VLANs), you can configure Network Policy Server (NPS) network policy to instruct the access servers to place members of Active Directory® groups on VLANs.
Before configuring network policy in NPS for VLANs, create groups of users in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) that you want to assign to specific VLANs. Then when you run the New Network Policy wizard, add the Active Directory group as a condition of the network policy.
You can create a separate network policy for each group that you want to assign to a VLAN. For more information, see Create a Group for a Network Policy.
When you configure network policy for use with VLANs, you must configure the RADIUS standard attributes Tunnel-Medium-Type, Tunnel-Pvt-Group-ID, and Tunnel-Type. Some hardware vendors also require the use of the RADIUS standard attribute Tunnel-Tag.
To configure these attributes in a network policy, use the New Network Policy wizard to create a network policy. You can add the attributes to the network policy settings while running the wizard or after you have successfully created a policy with the wizard.
Note
- To add the attributes after you have created the network policy with the wizard, locate the policy in the NPS console and double-click the policy to open it. Click the Settings tab in the policy properties, ensure that RADIUS Attributes - Standard is selected, and then click Add. In the Add Attribute dialog box, add the following attributes.
Tunnel-Medium-Type. Select a value appropriate to the previous selections you made while running the New Network Policy wizard. For example, if the network policy you are configuring is a wireless policy, in Attribute Value, select 802 (Includes all 802 media plus Ethernet canonical format).
Tunnel-Pvt-Group-ID. Enter the integer that represents the VLAN number to which group members will be assigned. For example, if you want to create a Sales VLAN for your sales team by assigning team members to VLAN 4, type the number 4.
Tunnel-Type. Select the value Virtual LANs (VLAN).
Tunnel-Tag. Some hardware devices do not require this attribute. If your hardware device requires this attribute, obtain this value from your hardware documentation.
MichelZMichelZNot the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged vpnvlanrrasdynamic-vlan-assignment or ask your own question.
ON THIS PAGE
IEEE 802.1X standard for port-based networkaccess control and protects Ethernet LANs from unauthorized user access.It blocks all traffic to and from a supplicant (client) at the interfaceuntil the supplicant's credentials are presented and matched on theauthentication server (a RADIUS server). When the supplicant is authenticated,the switch stops blocking access and opens the interface to the supplicant.Read this topic for more information.
802.1X for Switches Overview
How 802.1X Authentication Works
802.1X authentication works by using an authenticator portaccess entity (the switch) to block ingress traffic from a supplicant(end device) at the port until the supplicant's credentials are presentedand match on the authentication server (a RADIUS server). When authenticated,the switch stops blocking traffic and opens the port to the supplicant.
The end device is authenticated in single-secure supplicant mode, or Note
Configuring a VoIP VLAN on private VLAN (PVLAN) interfaces isnot supported.
RADIUS accounting—Sends accounting information tothe RADIUS accounting server. Accounting information is sent to theserver whenever a subscriber logs in or logs out and whenever a subscriberactivates or deactivates a subscription.
RADIUS server attributes for 802.1X—The
The following features are supported to authenticate devicesthat are not 802.1X-enabled:
Static MAC bypass—Provides a bypass mechanism toauthenticate devices that are not 802.1X-enabled (such as printers).Static MAC bypass connects these devices to 802.1X-enabled ports,bypassing 802.1X authentication.
MAC RADIUS authentication—Provides a means to permithosts that are not 802.1X-enabled to access the LAN. MAC-RADIUS simulatesthe supplicant functionality of the client device, using the MAC addressof the client as username and password.
802.1X Authentication on Trunk Ports
Starting in Junos OS Release 18.4R1, you can configure802.1X authentication on trunk interfaces, which allows the networkaccess device (NAS) to authenticate an access point (AP) or anotherconnected Layer 2 device. An AP or switchconnected to the NAS will support multiple VLANs, so must connectto a trunk port. Enabling 802.1X authentication on the trunk interfaceprotects the NAS from a security breach in which an attacker mightdisconnect the AP and connect a laptop to get free access to networkfor all the configured VLANs.
Please note the following caveats when configuring 802.1X authenticationon trunk interfaces.
Only single and single-secure supplicant modes are supportedon trunk interfaces.
You must configure 802.1X authentication locally on thetrunk interface. If you configure 802.1X authentication globally usingthe server-fail-voip).
Authentication on trunk port is not supported using captiveportal.
Authentication on trunk port is not supported on aggregatedinterfaces.
Configuration of 802.1X authentication on interfaces thatare members of private VLANs (PVLANs) is not supported on trunk ports.
See also
Configuring 802.1X Interface Settings (CLI Procedure)
IEEE 802.1X authentication provides network edge security,protecting Ethernet LANs from unauthorized user access by blockingall traffic to and from a supplicant (client) at the interface untilthe supplicant's credentials are presented and matched on the
[edit protocols dot1x]
user@switch# interface-name supplicant multipleMultiple supplicant mode is not supported on trunk interfaces.
[edit protocols dot1x]
user@switch# interface-name reauthentication interval set authenticator interface seconds[edit protocols dot1x]
user@switch# interface-name server-timeoutset authenticator interface seconds[edit protocols dot1x]
user@switch# interface-name maximum-requestsset authenticator interface numberThis setting specifies the number of attempts before theswitch puts the interface in a HELD state.
See also
Understanding RADIUS-Initiated Changes to an Authorized UserSession
When using an authentication service that isbased on a client/server RADIUS model, requests are typically initiatedby the client and sent to the RADIUS server. There are instances inwhich a request might be initiated by the server and sent to the clientin order to dynamically modify an authenticated user session alreadyin progress. The client that receives and processes the messages isthe switch, which acts as the network access server, or NAS. The servercan send the switch a Disconnect message requesting to terminate asession, or a Change of Authorization (CoA) message requesting tomodify the session authorization attributes.
The switch listens for unsolicited RADIUS requests on UPD port3799, and accepts requests only from a trusted source. Authorizationto send a Disconnect or CoA request is determined based on the sourceaddress and the corresponding shared secret, which must be configuredon the switch as well as on the RADIUS server. For more informationabout configuring the source address and shared secret on the switch,see Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
Disconnect Messages
The RADIUS server sends a Disconnect-Request message to theswitch in order to terminate a user session and discard all associatedsession context. The switch responds to a Disconnect-Request packetwith a Disconnect-ACK message if the request is successful, that is,all associated session context is discarded and the user session isno longer connected, or with a Disconnect-NAK packet if the requestfails, that is, the authenticator is unable to disconnect the sessionand discard all associated session context.
In Disconnect-Request messages, RADIUS attributes are used touniquely identify the switch (NAS) and the user session. The combinationof NAS identification attributes and session identification attributesincluded in the message must match at least one session for the requestto be successful; otherwise, the switch responds with a Disconnect-NAKmessage. A Disconnect-Request message can contain only NAS and sessionidentification attributes; if any other attributes are included, theswitch responds with a Disconnect-NAK message.
Change of Authorization Messages
Change of Authorization (CoA) messages contain information fordynamically modifying the authorization attributes for a user sessionto change the authorization level. This occurs as part of a two-stepauthentication process, in which the endpoint is first authenticatedusing MAC RADIUS authentication, and is then profiled based on thetype of device. The CoA message is used to apply an enforcement policythat is appropriate for the device, typically by changing the datafilters or the VLAN.
The switch responds to a CoA message with a CoA-ACK messageif the authorization change is successful, or a with CoA-NAK messageif the change is unsuccessful. If one or more authorization changesspecified in a CoA-Request message cannot be carried out, the switchresponds with a CoA-NAK message.
In CoA-Request messages, RADIUS attributes are used to uniquelyidentify the switch (acting as the NAS) and the user session. Thecombination of NAS identification attributes and session identificationattributes included in the message must match the identification attributesof at least one session for the request to be successful; otherwise,the switch responds with a CoA-NAK message.
CoA-Request packets also include the session authorization attributesthat will be modified if the request is accepted. The supported sessionauthorization attributes are listed below. The CoA message can containany or all of these attributes. If any attribute is not included aspart of the CoA-Request message, the NAS assumes that the value forthat attribute is to remain unchanged.
Filter-ID
Tunnel-Private-Group-ID
Juniper-Switching-Filter
Juniper-VoIP-VLAN
Session-Timeout
CoA Request Port Bounce
When a CoA message is used to change the VLAN for an authenticatedhost, end devices such as printers do not have a mechanism to detectthe VLAN change, so they do not renew the lease for their DHCP addressin the new VLAN. Startingin Junos OS Release 17.3, the port bounce feature can be used to forcethe end device to initiate DHCP re-negotiation by causing a link flapon the authenticated port.
The command to bounce the port is sent from the RADIUS serverusing a Juniper Networks vendor-specific attribute (VSA). The portis bounced if the following VSA attribute-value pair is received inthe CoA message from the RADIUS server:
Juniper-AV-Pair = “Port-Bounce”
To enable the port bounce feature, you must update the Junosdictionary file (juniper.dct) onthe RADIUS server with the Juniper-AV-Pair VSA. Locate the dictionaryfile and add the following text to the file:
For more information about adding the VSA, consult the FreeRADIUSdocumentation.
You can disable the feature by configuring the edit protocols dot1x authenticator interface interface-namemac-radius] hierachy level.
Error-Cause Codes
When a disconnect or CoA operation is unsuccessful, an Error-Causeattribute (RADIUS attribute 101) can be included in the response messagesent by the NAS to the server to provide detail about the cause ofthe problem. If the detected error does not map to one of the supportedError-Cause attribute values, the router sends the message withoutan error-cause attribute. See Table 1 for descriptions of error-cause codes that can be included in responsemessages sent from the NAS.
Table 1: Error-Cause Codes(RADIUS Attribute 101)
Code | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
201 | Residual session context removed | Sent in response to a Disconnect-Request message if one or moreuser sessions are no longer active, but residual session context wasfound and successfully removed. This code is sent only within a Disconnect-ACKmessage. |
401 | Unsupported attribute | The request contains an attribute that is not supported (forexample, a third-party attribute). |
402 | Missing attribute | A critical attribute (for example, the session identificationattribute) is missing from a request. |
403 | NAS identification mismatch | Request contains one or more NAS identification attributes thatdo not match the identity of the NAS receiving the request. |
404 | Invalid request | Some other aspect of the request is invalid—for example,if one or more attributes are not formatted properly. |
405 | Unsupported service | The Service-Type attribute included with the request containsan invalid or unsupported value. |
406 | Unsupported extension | The entity receiving the request (either an NAS or a RADIUSproxy) does not support RADIUS-initiated requests. |
407 | Invalid attribute value | The request contains an attribute with an unsupported value. |
501 | Administratively prohibited | The NAS is configured to prohibit honoring of Disconnect-Requestor CoA-Request messages for the specified session. |
503 | Session context not found | The session context identified in the request does not existon the NAS. |
504 | Session context not removable | The subscriber identified by attributes in the request is ownedby a component that is not supported. This code is sent only withina Disconnect-NAK message. |
506 | Resources unavailable | A request could not be honored because of lack of availableNAS resources (such as memory). |
507 | Request initiated | The CoA-Request message includes a Service-Type attribute witha value of Authorize Only. |
508 | Multiple session selection unsupported | The session identification attributes included in the requestmatch multiple sessions, but the NAS does not support requests thatapply to multiple sessions. |
Filtering 802.1X Supplicants by Using RADIUS Server Attributes
There are two ways to configure the a RADIUS server withport firewall filters (Layer 2 firewall filters):
Include one or more filter terms in the Juniper-Switching-Filterattribute. The Juniper-Switching-Filter attribute is a vendor-specificattribute (VSA) listed under attribute ID number 48 in the Juniperdictionary on the RADIUS server. Use this VSA to configure simplefilter conditions for 802.1X authenticated users. Nothing needs tobe configured on the switch; all of the configuration is on the RADIUSserver.
Configure a local firewall filter on each switch and applythat firewall filter to users authenticated through the RADIUS server.Use this method for more complex filters. The firewall filter mustbe configured on each switch.
Note If the firewall filter configuration is modified afterusers are authenticated using the 802.1X authentication, then theestablished 802.1X authentication session must be terminated and re-establishedfor the firewall filter configuration changes to take effect.
This topic includes the followingtasks:
Configuring Firewall Filters on the RADIUS Server
You can configure simple filter conditions by using the Juniper-Switching-Filterattribute in the Juniper dictionary on the RADIUS server. These filtersare sent to a switch whenever a new user is authenticated successfully.The filters are created and applied on all EX Series switches thatauthenticate users through that RADIUS server without the need foryou to configure anything on each individual switch.
NoteThis procedure describes using FreeRADIUS software toconfigure the Juniper-Switching-Filter VSA. For specific informationabout configuring your server, consult the AAA documentation includedwith your server.
To configure the Juniper-Switching-Filter attribute, enter oneor more filter terms by using the CLI for the RADIUS server. Eachfilter term consists of match conditions with a corresponding action.Enter the filter terms enclosed within quotation marks (' ') by usingthe following syntax:
More than one match condition can be included in a filter term.When multiple conditions are specified in a filter term, they mustall be fulfilled for the packet to match the filter term. For example,the following filter term requires a packet to match both the destination IP address and the destination MAC address to meetthe term criteria:
Multiple filter terms should be separated with commas—forexample:
See Juniper-Switching-Filter VSA Match Conditions and Actions for definitions of match conditions and actions.
NoteOn EX9200 switches, and in a Junos Fusion Enterprise withEX9200 as the aggregate device, the dynamic firewall filter is strictlyapplied for all IP packets. If the filter is configured to allow onlya specific destination IP address, packets with other IP addressesas the destination IP will be dropped per the filter rules. This includesany IP protocol packets, such as DHCP, IGMP and ARP packets.
To configure match conditions on the RADIUS server:
- Verify that the Juniper dictionary is loaded on your RADIUSserver and includes the filtering attribute Juniper-Switching-Filter (attribute ID 48):
[root@freeradius]# cd /usr/local/etc/raddb
Juniper-Switching-Filter = 'Match Source-dot1q-tag10 Action deny' To deny access based on a destination IP address:
[root@freeradius]# vi usersFor each relevant user, add the Juniper-Switching-Filter attribute:
cd /usr/local/etc/raddb
Juniper-Switching-Filter = 'Match Destination-mac00:04:0f:fd:ac:fe, Ip-protocol 2, forwarding-class high, Action loss-priorityhigh'Note For the forwarding-class option to be applied,the forwarding class must be configured on the switch and the packetloss priority specified. If it is not configured on the switch, thisoption is ignored. You must specify both the forwarding class andthe packet loss priority.
- Stop and restart the RADIUS process to activate the configuration.
Applyinga Locally Configured Firewall Filter from the RADIUS Server
You can apply a port firewall filter (Layer 2 firewallfilter) to user policies centrally from the RADIUS server. The RADIUSserver can then specify the firewall filters that are to be appliedto each user that requests authentication, reducing the need to configurethe same firewall filter on multiple switches. Use this method whenthe firewall filter contains a large number of conditions or you wantto use different conditions for the same filter on different switches.The firewall filters must be configured on each switch.
For more information about firewall filters, see Firewall Filters for EX Series Switches Overview.
To apply a port firewall filter centrally from the RADIUS server:
NoteIf port firewall filters are also configured locally forthe interface, then the firewall filters configured by using VSAstake precedence if they conflict with the locally configured portfirewall filters. If there is no conflict, they are merged.
- Create the firewall filter on the local switch. See Configuring Firewall Filters (CLI Procedure) for more information on configuring a port firewall filter.
- On the RADIUS server, open the
usersfile to display the local user profiles of the end devices to whichyou want to apply the filter:[root@freeradius]#
vi users - Apply the filter to each user profile by adding the Filter-IDattribute with the filter name as the attribute value:
For example, the user profile below for filter1:
Note Multiple filters are not supported on a single interface.However, you can support multiple filters for multiple users thatare connected to the switch on the same interface by configuring asingle filter with policies for each of those users.
- Stop and restart the RADIUS process to activate the configuration.
See also
Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX SeriesSwitch
802.1X is the IEEE standard for port-based networkaccess control (PNAC). You use 802.1X to control network access. Onlyusers and devices providing credentials that have been verified againsta user database are allowed access to the network. You can use a RADIUSserver as the user database for 802.1X authentication, as well asfor MAC RADIUS authentication.
This example describes how to connect a RADIUS server to anEX Series switch, and configure it for 802.1X:
Requirements
This example uses the following software and hardwarecomponents:
Junos OS Release 9.0 or later for EX Series switches
One EX Series switch acting as an authenticator port accessentity (PAE). The ports on the authenticator PAE form a control gatethat blocks all traffic to and from supplicants until they are authenticated.
One RADIUS authentication server that supports 802.1X.The authentication server acts as the backend database and containscredential information for hosts (supplicants) that have permissionto connect to the network.
Before you connect the server to the switch,be sure you have:
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on theswitch. See the documentation that describes setting up basic bridgingand a VLAN for your switch. If you are using a switch that supportsthe Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style, see Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch with ELS Support . For all other switches,see Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch.
Note For more about ELS, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
Configured users on the RADIUS authentication server.
Overview and Topology
The EX Series switch acts as an authenticator PAE. It blocksall traffic and acts as a control gate until the supplicant (client)is authenticated by the server. All other users and devices are deniedaccess.
Figure 1 shows one EX4200 switchthat is connected to the devices listed in Table 2.
Table 2: Components of the Topology
| Property | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware | EX4200 access switch, 24 Gigabit Ethernet ports: 8 PoEports (ge-0/0/0 through ge-0/0/7) and 16 non-PoE ports (ge-0/0/8 throughge-0/0/23) |
VLAN name | default |
One RADIUS server | Backend database with an address 10.0.0.100 connectedto the switch at port ge-0/0/10 |
In this example, connect the RADIUS server to access port ge-0/0/10on the EX4200 switch. The switch acts as the authenticator and forwardscredentials from the supplicant to the user database on the RADIUSserver. You must configure connectivity between the EX4200 and theRADIUS server by specifying the address of the server and configuringthe secret password. This information is configured in an access profileon the switch.
NoteFor more information about authentication, authorization,and accounting (AAA) services, see the Junos OS System Basics Configuration Guide.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly connect the RADIUS server to theswitch, copy the following commands and paste them into the switchterminal window:
set access radius-server 10.0.0.200 secret juniperset access profile profile1 radius authentication-server[10.0.0.100 10.0.0.200]Step-by-Step Procedure
- Define the address of the servers, and configure the secretpassword. The secret password on the switch must match the secretpassword on the server:
[edit]
user@switch# set access radius-server 10.0.0.200secret juniper - Configure the authentication order, making radius the first method of authentication:
[edit]
user@switch# set accessprofile profile1 radius authentication-server [10.0.0.100 10.0.0.200]
Results
Display the results of the configuration:
Verification
To confirm that the configuration is workingproperly, perform these tasks:
Verify That the Switch and RADIUS Server Are Properly Connected
Purpose
Verify that the RADIUS server is connected to the switchon the specified port.
Action
Ping the RADIUS server to verify the connection betweenthe switch and the server:
Meaning
ICMP echo request packets are sent from the switchto the target server at 10.0.0.100 to test whether the server is reachableacross the IP network. ICMP echo responses are being returned fromthe server, verifying that the switch and the server are connected.
See also
Understanding Dynamic Filters Based on RADIUS Attributes
You can use RADIUS server attributes to implement port firewallfilters on a RADIUS authentication server. These filters can be dynamicallyapplied to supplicants that request authentication through that server.RADIUS server attributes are clear-text fields encapsulated in Access-Acceptmessages sent from the authentication server to the switch when asupplicant connected to the switch is successfully authenticated.The switch, acting as the authenticator, uses the information in theRADIUS attributes to apply the related filters to the supplicant.Dynamic filters can be applied to multiple ports on the same switch,or to multiple switches that the use same authentication server, providingcentralized access control for the network.
You can define firewall filters directly on the RADIUS serverby using the Juniper-Switching-Filter attribute, which is a RADIUSattribute specific to Juniper Networks, also known as a vendor-specificattribute (VSA). VSAs are described in RFC 2138, RemoteAuthentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS). The Juniper-Switching-FilterVSA is listed under attribute ID number 48 in the Juniper dictionaryon the RADIUS server, with the vendor ID set to the Juniper NetworksID number 2636. Using this attribute, you define filters on theauthentication server, which are applied on all switches that authenticatesupplicants through that server. This method eliminates the need toconfigure the same filters on multiple switches.
Alternatively, you can apply a port firewall filter to multipleports on the same switch by using the Filter-ID attribute, which isRADIUS attribute ID number 11. To use the Filter-ID attribute,you must first configure a filter on the switch, and then add thefilter name to user policies on the RADIUS server as the value ofthe Filter-ID attribute. When a supplicant defined in one of thosepolicies is authenticated by the RADIUS server, the filter is appliedto the switch port that has been authenticated for the supplicant.Use this method when the firewall filter has complex conditions, orif you want to use different conditions for the same filter on differentswitches. The filter named in the Filter-ID attribute must be configuredlocally on the switch at the [VLAN.
Tunnel-Medium-Type—Defined as RADIUS attribute type 65.The value should be set to Microsoft Nps Radius
This example also applies to QFX5100 switches.
Junos OS Release 9.3 or later for EX Series switches
One EX Series switch acting as an authenticator port accessentity (PAE). The ports on the authenticator PAE form a control gatethat blocks all traffic to and from supplicants until they are authenticated.
One RADIUS authentication server that supports 802.1X.The authentication server acts as the backend database and containscredential information for hosts (supplicants) that have permissionto connect to the network.
Before you connect the server to the switch,be sure you have:
Performed basic bridging and VLAN configuration on theswitch. See the documentation that describes setting up basic bridgingand a VLAN for your switch. If you are using a switch that supportsthe Enhanced Layer 2 Software (ELS) configuration style, see Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch with ELS Support or Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN on Switches. For all other switches, seeExample: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch.
Note For more about ELS, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLI.
Set up a connection between the switch and the RADIUSserver. See Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch.
Configured users on the authentication server.
Overview and Topology
A RADIUS server timeout occurs if no authentication RADIUS serversare reachable when a supplicant logs in and attempts to access theLAN. Using server fail fallback, you configure alternative optionsfor supplicants attempting LAN access. You can configure the switchto accept or deny access to supplicants or to maintain the accessalready granted to supplicants before the RADIUS server timeout. Additionally,you can configure the switch to move supplicants to a specific VLANif a RADIUS timeout occurs or if the RADIUS server sends an EAP Access-Rejectmessage.
Figure 2 showsthe topology used for this example. The RADIUS server is connectedto the EX4200 switch on access port ge-0/0/10. The switchacts as the authenticator port access entity (PAE) and forwards credentialsfrom the supplicant to the user database on the RADIUS server. Theswitch blocks all traffic and acts as a control gate until the supplicantis authenticated by the authentication server. A supplicant is connectedto the switch through interface ge-0/0/1.
NoteThis figure also applies to QFX5100 switches.
Table 3 describes the components in this topology.
Table 3: Components of theTopology
| Property | Settings |
|---|---|
Switch hardware | EX4200 access switch, 24 Gigabit Ethernet ports: 16 non-PoEports and 8 PoE ports. |
VLAN names | default VLAN vlan-sf VLAN |
Supplicant | Supplicant attempting access on interface ge-0/0/1 |
One RADIUS server | Backend database with an address of 10.0.0.100 connected to the switch at port ge-0/0/10 |
In this example, configure interface ge-0/0/1 to move a supplicantattempting access to the LAN during a RADIUS timeout to another VLAN.A RADIUS timeout prevents the normal exchange of EAP messages thatcarry information from the RADIUS server to the switch and permitthe authentication of a supplicant. The default VLAN is configuredon interface ge-0/0/1. When a RADIUS timeout occurs, supplicants onthe interface will be moved from the default VLAN to the VLAN namedvlan-sf.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure server fail fallbackon the switch, copy the following commands and paste them into theswitch terminal window:
Define the VLAN to which supplicants are diverted:[edit protocols dot1x authenticator]
user@switch# show vlans command will containadditional information. If your switch runs software that supportsELS, see show vlans.For ELS details, see Using the Enhanced Layer 2 Software CLIAction
Display the VLANs configured on the switch; the interface ge-0/0/1.0 is a member of the default VLAN:
Display 802.1X protocol information on the switch toview supplicants that are authenticated on interface show vlans command displays interface ge-0/0/1.0 as a member of the default VLAN. The
However, this fallback configuration is complicated by the factthat the OAC supplicant and RADIUS server are using EAP-TTLS. EAP-TTLScreates a secure encrypted tunnel between the server and the end deviceto complete the authentication process. When the user enters incorrectlogin credentials, the RADIUS server sends EAP failure messages directlyto the client through this tunnel. The EAP failure message causesthe client to restart the authentication procedure, so that the switch’s802.1X authentication process tears down the session that was establishedwith the switch using the server-reject VLAN. You can enable the remedialconnection to continue by configuring:
eapol-block—Enable the EAPoL block timeron the 802.1X interface that is configured to belong to the server-rejectVLAN. The block timer causes the authentication port access entityto ignore EAP start messages from the client, attempting to restartthe authentication procedure.
NoteThe EAPoL block timer is triggered only after the configurednumber of allowed reattempts (using the retries option) onthe 802.1X interface have been exhausted. You can configure retries to specify the number of times the switch attempts to authenticatethe port after an initial failure. The default is three retries.
block-interval—Configure the amount oftime that you want the EAPoL block timer to continue to ignore EAPstart messages. If you do not configure the block interval, the EAPoLblock timer defaults to 120 seconds.
When the 802.1X interface ignores the EAP start messages fromthe client, the switch allows the existing remedial session that wasestablished through the server-reject VLAN to remain open.
These configuration options apply to single, single-secure,and multiple supplicant authentication modes. In this example, the802.1X interface is configured in single supplicant mode.
Figure 3 shows an EX Seriesswitch connecting an OAC end device to a RADIUS server, and indicatesthe protocols being used to connect the network entities.
NoteThis figure also applies to QFX5100 switches.
Table 4 describesthe components in this OAC deployment:.
Table 4: Components of the OAC Deployment
Property Settings Switch hardware
EX Series switch
VLANs
default
server-reject-vlan: VLAN name is remedial and VLAN ID is 700
802.1X interface
ge-0/0/8
OAC supplicant
EAP-TTLS
One RADIUS authentication server
EAP-TTLS
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure the fallback optionsfor EAP-TTLS and OAC supplicants, copy the following commands andpaste them into the switch terminal window:
[edit]
set protocols dot1xauthenticator interface ge-0/0/8 retries 4
set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/8 server-reject-vlaneapol-block
Configure a VLAN that will function as the server-rejectVLAN to provide limited LAN access for users who have entered incorrectlogin credentials:Configure the number of times for the client to be promptedfor username and password before an incorrect login is directed tothe server-reject VLAN:[edit protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/8]
user@switch# set server-reject-vlan remedialEnable the EAPoL block timer on the 802.1X interface thatis configured to belong to the server-reject VLAN. [edit protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/8]
user@switch# set server-reject-vlan block-interval 130Results
ResultsCheck the results of the configuration:
Verification
VerificationTo confirm that the configuration and the fallbackoptions are working correctly, perform this task:
Verifying the Configuration of the 802.1X Interface
Verifying the Configuration of the 802.1X InterfacePurpose
PurposeVerify that the 802.1X interface is configured withthe desired options.
Action
Actionuser@switch> show dot1x ge-0/0/8 detail command outputshows that the ge-0/0/8 interface is in the Authenticated state and that it is using the remedial VLAN.See also
Monitoring 802.1X Authentication
Purpose
NoteThis topic applies only to the J-Web Application package.
J-Web Applicationpackage Release 14.1X53-A2 does not support 802.1X authenticationon EX4600 switches.
Use the monitoring feature to display details of authenticatedusers and users that failed authentication.
Action
To display authentication details in the J-Web interface,select Security > show dot1x interface detail | display xml
<interface> | display xml
Dynamic Vlan Assignment Microsoft Nps Radius Server Login
You can also specify an interface for which the details mustbe displayed.
See also
Verifying 802.1X Authentication
Purpose
Verify that supplicants are being authenticated onan interface on a switch with the interface configured for 802.1Xauthentication, and display the method of authentication being used.
Action
Display detailed information about an interface configuredfor 802.1X (here, the interface is ge-0/0/16):
user@switch> show dot1x interfacedetail command shows that the Radius in the output. When RADIUS authenticationis used, the supplicant is configured on the RADIUS server, the RADIUSserver communicates this to the switch, and the switch opens LAN accesson the interface to which the supplicant is connected. The sampleoutput also shows that the supplicant is connected to VLAN v200.Other 802.1X authentication methods supported on EX Series switchesin addition to RADIUS authentication are:
Guest VLAN—A nonresponsive host is granted Guest-VLANaccess.
MAC Radius—A nonresponsive host is authenticatedbased on its MAC address. The MAC address is configured as permittedon the RADIUS server, the RADIUS server notifies the switch that theMAC address is a permitted address, and the switch grants LAN accessto the nonresponsive host on the interface to which it is connected.
Server-fail deny—If the RADIUS servers time out,all supplicants are denied access to the LAN, preventing traffic fromthe supplicant from traversing through the interface. This is thedefault.
Server-fail permit—When the RADIUS server is unavailable,a supplicant is still permitted access to the LAN as if the supplicantwere successfully authenticated by the RADIUS server.
Server-fail use-cache—If the RADIUS servers timeout during reauthentication, previously authenticated supplicantsare granted LAN access, but new supplicants are denied LAN access.
Server-fail VLAN—A supplicant is configured to bemoved to a specified VLAN if the RADIUS server is unavailable to reauthenticatethe supplicant. (The VLAN must already exist on the switch.)
See also
Troubleshooting Authentication of End Devices on EX SeriesSwitches
Problem
Description: End devices configured using static MACaddresses lose connection to the switch after the clear dot1x interfacecommand is run to clear all learned MAC addresses.
Before clearing MAC addresses:
Microsoft Radius Server
To clear MAC addresses:
After clearing MAC addresses:
Note that there are no end devices on the authentication bypasslist.
Cause
Static MAC addresses are treated the same as other learnedMAC addresses on an interface. When the clear dot1x interface commandis run, it clears all learned MAC addresses from the interface, includingthe static MAC bypass list (also known as the exclusion list).
Windows Server 2016 Nps Radius
Solution
If you run the clear dot1x interfaces command foran interface that has static MAC addresses configured for authenticationbypass, re-add the static MAC addresses to the static MAC bypass list.
See also
Related Documentation
DescriptionStarting in Junos OS Release 18.4R1, you can configure802.1X authentication on trunk interfaces, which allows the networkaccess device (NAS) to authenticate an access point (AP) or anotherconnected Layer 2 device. Startingin Junos OS Release 17.3, the port bounce feature can be used to forcethe end device to initiate DHCP re-negotiation by causing a link flapon the authenticated port.J-Web Applicationpackage Release 14.1X53-A2 does not support 802.1X authenticationon EX4600 switches.